Foreign investors can carry on business in Hong Kong through multiple business vehicles, including:
- A company incorporated in Hong Kong;
- A branch office of the foreign corporation;
- A representative office;
- Sole proprietorship; and
- Partnership.
While some options are more commonly adopted than others, investors are advised to choose the most appropriate business structure based on the pros and cons of each option.
Hong Kong companies
Foreign investors can establish their presence in Hong Kong by setting up a Hong Kong company. Companies incorporated in Hong Kong can be limited or unlimited and can be public or private. Described below are five types of companies that may be formed under the Companies Ordinance (Cap. 622):
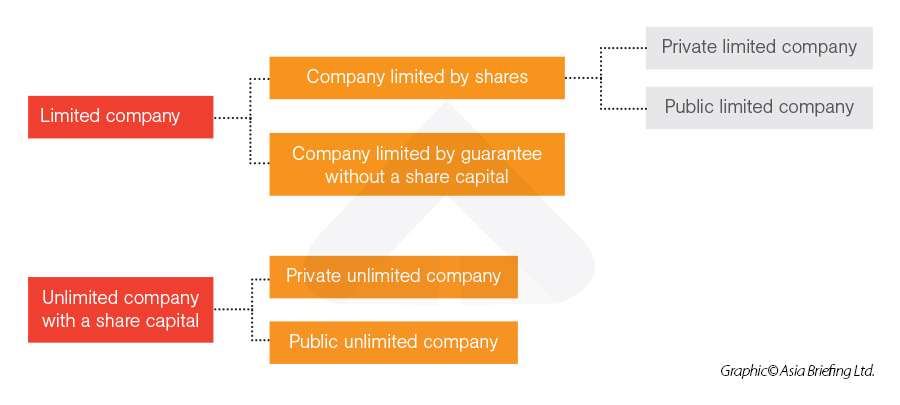
- Private companies limited by shares (private limited company);
- Public companies limited by shares (public limited company);
- Companies limited by guarantee without a share capital;
- Private unlimited companies with a share capital (private unlimited company); and
- Public unlimited companies with a share capital (public unlimited company).
Private limited company (Private companies limited by shares)
A company limited by shares has a share capital. The shares are issued to shareholders, and the liability of its shareholders will be limited to the unpaid subscription price for the shares. This is most suitable for a company that carries on a business for profit-making purposes.
A private limited company is a company limited by shares which:
- Restricts the ability of its members to transfer shares;
- Limits the number of members to 50 (not including employees or former employees); and,
- Do not issue invitations to the public to subscribe for shares or debentures of the company.
Most small to medium-sized companies are set up as private limited companies due to their many advantages, such as their separate legal entity, limited liability to members, positive image among banks and investors, and the convenience of ownership transfer.
Minimum capital requirements
No minimum share capital requirement
Setting up timeline
Within one week
Key positions
A company secretary, a director, a maximum of 50 shareholders, and a designated representative are required.
Public limited company
A public limited company is a company whose shares and debentures are offered to the public.
It is a public limited company if it is a limited liability company but does not fall into the scope of a private limited company or a company limited by guarantee.
Many public companies are listed on the Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited, and the statutory requirement for a public company is much stricter as it raises capital from the public. A medium to large private limited company may decide to transfer the company structure to a public limited company (thereby expanding its share base) – when they achieve significant growth in the industry.
Minimum capital requirements
No minimum share capital requirement
Setting up timeline
One hour to two working days for private companies incorporated online and four working days for offline companies incorporation
Key positions
- A board of directors consisting of two members minimum;
- A designated representative;
- A company secretary and;
- A minimum of one shareholder.
Private limited company (Private companies limited by guarantee without a share capital)
A company limited by guarantee does not have share capital, but the liability of its members is determined by the amount of assets they contribute. This type of company is most suitable for nonprofit activities, such as operating a nonprofit research institute. It is not an appropriate structure for a business undertaken for profit-making purposes.
Incorporation fees
The Companies Registry charges an incorporation fee based on the number of members in the company. The price is HK$170 (US$21) for companies with 25 members or fewer, HK$340 (US$43) for those with more than 25 members but not exceeding 100, and an additional HK$20 (US$2.5) for every 50 members or less after the first 100 members.
It is worth noting that if the company is exempt from profits tax under section 88 of the Inland Revenue Ordinance, the business registration fee with the IRD is not applicable.
Setting up timeline
4-6 weeks to 6 months or more depending on business activity.
Key positions
- One member, two individual directors, and one corporate secretary are required.
- The member may be an individual or a corporation, with no nationality restrictions.
- The company secretary can be a Hong Kong resident or a corporate entity registered in Hong Kong.
- A designated representative who is a Hong Kong resident or qualified professional firm must be appointed.
- Each member must declare the guaranteed amount.
Other requirements
- The registered office address must be located within Hong Kong.
- Annual audited financial statements must be submitted to the Companies Registry, which is accessible to the public.
- Profit distribution is prohibited.
- Articles of association are mandatory.
Ongoing obligations
A series of ongoing responsibilities outlined in the Companies Ordinance encompass:
- Maintaining comprehensive records of debenture holders, members, directors, and company secretaries.
- Ensuring the upkeep of accurate accounting books, subject to annual audits.
- Organizing annual general meetings as required.
- Submitting annual returns to the Companies Registry and remitting the annual registration fee to the Inland Revenue Department for the Company's Business Registration renewal unless the company qualifies for exemption from profits tax under Section 88 of the Inland Revenue Ordinance.
- Preparing audited financial statements to present during the annual general meetings.
- Renewing the business registration one month before its expiry annually or once every three years, depending on whether the certificate is valid for one year or three years.
- Filing annual tax return with the Inland Revenue Department including financial statements and tax computations one month from the date of issue.
Unlimited company
The essential difference between a limited and unlimited company lies in the absence of any ceiling on the amount of capital an individual can inject into an unlimited company. Investors are responsible for infusing funds into the company whenever necessary, and the sole method to prevent its financial downfall is the owners' continual investments.
Members of an unlimited company are not restricted in terms of their financial liabilities, similar to partnerships. However, unlike a partnership, an unlimited company is recognized as a distinct legal entity. Due to this resemblance, many startup businesses establish themselves as partnerships to avoid the complexities of registering and incorporating a company.
Branch offices
A branch office in Hong Kong lacks a distinct legal identity and is considered an extension of its overseas parent company. Consequently, the overseas parent company assumes full responsibility for all the debts and obligations incurred by the branch office.
A foreign corporation wishing to establish a Hong Kong branch office must register with the Companies Registry as a non-Hong Kong company and obtain a Business Registration Certificate.
Branch offices of foreign companies registered in Hong Kong are subject to the exact legal and tax requirements and ramifications as locally incorporated companies. The allowable business activities in Hong Kong and the applicable profit tax rate remain identical for foreign company branch offices and locally registered companies.
Although this option is generally not recommended due to the parent company's increased liability for branch offices, foreign investors may still favor this approach over establishing a subsidiary due to specific considerations:
- A branch office might be more tax efficient for the parent company under certain circumstances, such as when losses incur in the Hong Kong branch.
- Generally, the transfer of the shares of a foreign company operating a branch in Hong Kong is not subject to stamp duty.
- A branch office is subject to limited compliance requirements under the Companies Ordinance.
- A branch office is not required to conduct a separate audit.
- A branch office can be terminated quickly by notifying the Company Registry.
Setting up timeline
12-14 working days
Minimum capital requirement
No minimum share capital requirement
Representative offices
Like a branch office, a representative office lacks a distinct legal identity. Instead, the parent overseas company assumes full responsibility for any debts and obligations incurred. However, it's important to note that a representative office is prohibited from engaging in profit-generating business activities; otherwise, it must undergo registration as a branch office. Its functions are limited to promotional efforts, communication, and market research.
While representative offices do not require registration with the Companies Registry, they must apply for a Business Registration Certificate through the Inland Revenue Department.
Compared to branches, representative offices may be preferable for foreign investors interested in exploring the Hong Kong market. This preference arises because representative offices are exempt from submitting profit tax returns in Hong Kong if they do not conduct profit-generating activities within the region.
Setting up timeline
2-3 working days
Minimum capital requirement
No minimum share capital requirement
Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the most straightforward and uncomplicated business structure, wholly owned and managed by a single individual. It lacks a distinct legal identity, with the sole proprietor entitled to all business profits while personally shouldering all liabilities. The sole requirement for establishing a sole proprietorship is obtaining a Business Registration Certificate.
Beyond its simplicity in setup, a sole proprietorship offers specific tax advantages. The sole proprietor can opt for "Personal Assessment" when filing their tax return for the year. This approach subjects the sole proprietorship's profits to the salary tax scheme, which benefits from generous allowances, deductions, and a potentially lower progressive tax rate than corporate taxation. Additionally, any business losses incurred within the sole proprietorship can be offset against the proprietor's other sources of income.
Conversely, a sole proprietorship is regarded as the riskiest business form due to the sole proprietor's joint liability for the business's debts. Personal assets are not shielded from these liabilities. Consequently, sole proprietorship is generally not recommended for investors.
Setting up timeline
1-2 working days
Minimum capital requirement
No minimum share capital requirement
Partnership
A partnership is a business arrangement in which two or more individuals collaborate to share profits.
Hong Kong recognizes two primary types of partnerships:
General partnerships
In a general partnership, partners possess complete property rights and bear personal liability for the debts and obligations incurred by the partnership. The primary procedural requirement for establishing a general partnership is obtaining a Business Registration Certificate.
Limited partnerships
In a limited partnership, at least one general partner must manage the partnership and assume total debt liability. Additionally, there can be one or more limited partners whose liability is limited to the capital they contribute to the partnership. Limited partners need the authority to manage or oversee the partnership's operations. Registering a limited partnership with the Companies Registry and obtaining a Business Registration Certificate is mandatory.
Partnerships offer distinct advantages over companies as they are generally easier to establish, maintain, and dissolve. They are subject to fewer regulatory compliance requirements. Moreover, partnerships can be highly effective at attracting talented employees, as individuals with valuable skills, knowledge, and expertise may have opportunities for advancement to become partners themselves.
Setting up timeline
- A limited partnership usually takes up to five working days to obtain a business registration.
- A general partnership usually requires one to two working days to obtain the business registration.
Minimum capital requirement
No minimum share capital requirement
Restrictions on foreign investment
Hong Kong does not subject foreign investments to special regulatory regimes or requirements per se. However, based on public interest, there are restrictions on voting control by non-Hong Kong residents and corporations in the broadcasting sector. Such restrictions are set out in the Broadcasting Ordinance (Cap. 562) and the Telecommunications Ordinance (Cap. 106). The government’s special industrial-land policy features somewhat more complex rules, but it is still less demanding than the policies of many other Asian investment centers.
Television
The Broadcasting Ordinance states that foreign ownership of a Hong Kong company with a license to broadcast domestic free television requires written consent from the Broadcasting Authority at three thresholds:
- Shareholding of 5-10 percent;
- Shareholding of 10-15 percent; or
- Shareholding of over 15 percent.
In addition, if foreign entities, in the aggregate, hold over 49 percent of voting control in such a company, their votes shall be subject to a formula as outlined in the Broadcasting Ordinance.
These restrictions do not apply to paid television or non-domestic television.
Radio
Foreign ownership in a company holding a sound broadcasting license must be at most 49 percent. Proper broadcasting licenses are exclusively available to Hong Kong-based firms, which cannot operate as subsidiaries of other companies.







