China’s Medical Beauty Industry: Challenges, Trends, and Opportunities
Amid a global economic slowdown, China’s medical beauty (also known as medical aesthetic) market has managed to stand out as one of the fastest-growing sectors worldwide. Fueled by a steady influx of capital, the industry has successfully established a well-defined and comprehensive industrial chain encompassing upstream manufacturers, medical aesthetic service providers, and end-users.
Despite its impressive growth, there is substantial untapped potential in the Chinese market, making the medical beauty industry a focal point within the larger beauty and healthcare sectors, as well as a primary area for consumption growth.
Meanwhile, China’s economic resilience has played a pivotal role in the gradual revival of consumer confidence. This resurgence is particularly evident in the field of medical beauty, where consumers’ pursuit of self-improvement, coupled with technological innovation and diversification of the consumer base, pushes the market forward.
As the competitive landscape within the medical aesthetic sector undergoes rapid transformation, the industry is poised to encounter unprecedented challenges and opportunities. In this intricate marketplace marked by fierce competition, understanding the core needs of medical aesthetic users and building trust emerges as the key to success in the next phase of market development.
Overview of China’s medical beauty market development
Market size
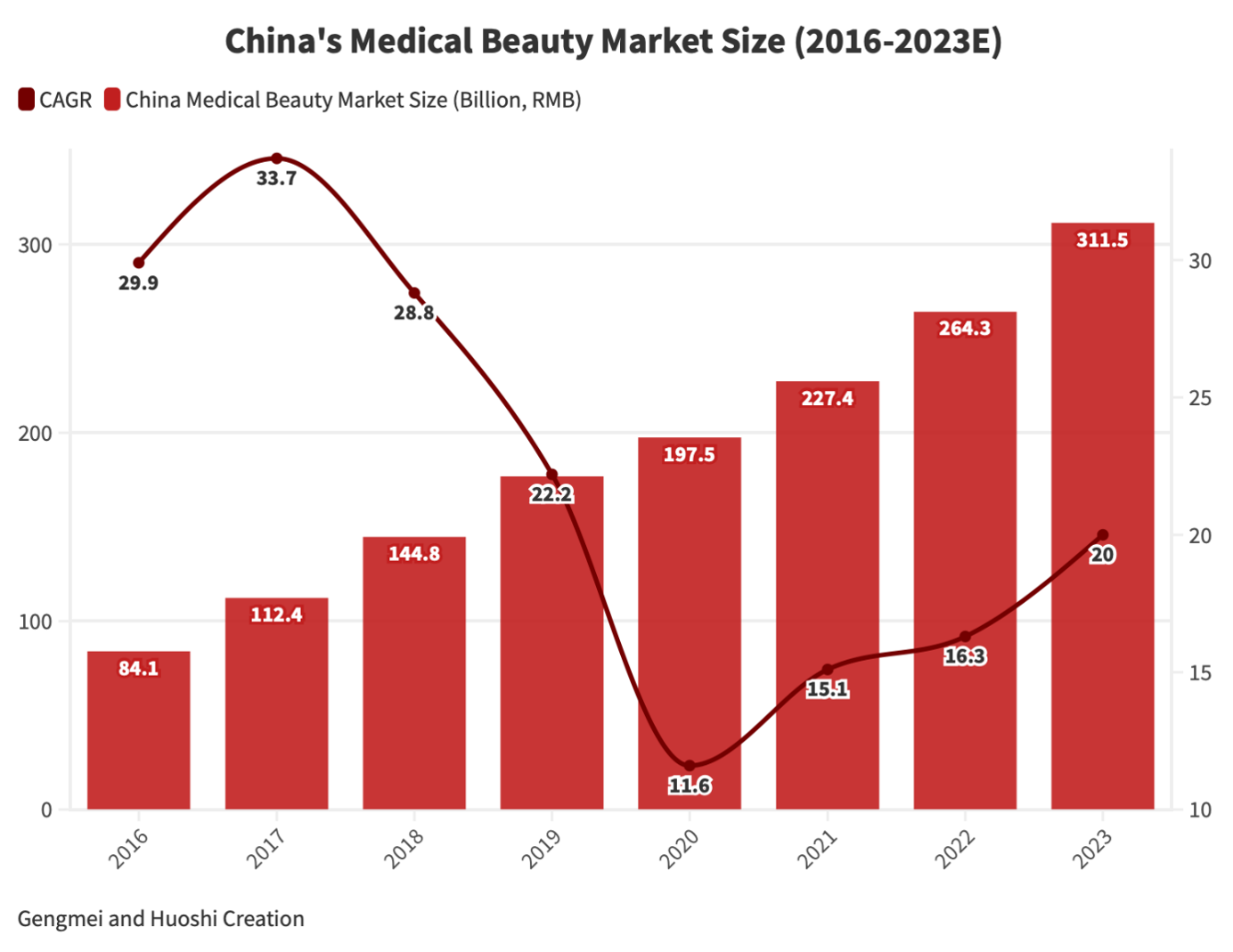
The Chinese medical beauty industry has experienced a growth rate higher than the global average, indicating significant potential for expansion. According to data from iResearch, in 2021, the Chinese medical beauty market reached a scale of RMB 227.4 billion (US$32 billion), with a growth rate of 15.1 percent. This growth outpaced the global average, constituting 21.9 percent of the total global medical beauty market.
Looking at the yearly compound growth, the Chinese medical beauty market expanded from RMB 84.1 billion (US$11.9 billion) in 2016 to RMB 197.5 billion (US$27.8 billion) in 2020, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.7 percent.
Despite experiencing robust growth in previous years, the industry faced a setback in 2022 due to the impact of pandemic control measures and a high infection rate towards the end of the year. Consequently, consumers’ shopping visit frequency and unit prices sharply declined, leading to a stagnation period. Notably, surgical treatments were particularly affected by these circumstances.
Nevertheless, industry experts anticipate a significant rebound in 2023, with the overall medical aesthetic market expected to grow by 20 percent. This resurgence is attributed to the post-pandemic recovery in consumer spending habits.
Looking beyond this recovery phase, the subsequent four years are anticipated to maintain a healthy CAGR of 15 percent, underscoring a continued positive trajectory for the development of the Chinese medical beauty industry.
Market segmentation
China’s medical beauty industry, marked by its dynamic growth, is characterized by a nuanced market segmentation that caters to diverse consumer preferences and needs. The segmentation of the medical beauty market in China can be understood through various lenses, including:
| China’s Medical Beauty Industry Key Market Segments | |
| Segment | Description |
| Product-based | Surgical and non-surgical procedures, injectables |
| Medical beauty equipment | Photon and light medical beauty devices |
| Service providers | Medical beauty service providers |
For this article, we will be mainly focusing on product-based segments.
Key domestic and foreign players
China’s thriving medical beauty industry is primarily concentrated in its most developed provinces. Notably, consumer activity is most pronounced in economically advanced cities like Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, as well as other first-tier and large cities.
The industry is marked by intense competition, coupled with a noticeable shift towards domestic substitution. At present, injection components, notably hyaluronic acid and botulinum toxin, occupy over 85 percent of the cosmetic fillers market.The increasing preference for local alternatives in the context of hyaluronic acid is becoming more pronounced, with 18 domestic brands gaining momentum and competing alongside three major foreign competitors. Noteworthy examples of these local alternatives include LG Yvoire by Hua Dong Medicine, Qoovon by Allergan, and ReLan by Goodmede, which have notably emerged as top sellers in the market. Domestic brands like Imeik (爱美客), Huaxi (华熙), and Haohai (昊海) have secured 14 percent, 8.1 percent and 6 percent market shares, respectively. This trend reflects consumers’ growing inclination to choose Chinese brands over international ones for their hyaluronic acid-based aesthetic treatments.
Meanwhile, as of the end of 2022, the high-end market for botulinum toxin products continues to be dominated by foreign brands. Notably, industry leaders such as Allergan, Dysport by Ipsen (operated exclusively by Goodmede), and Hugel’s Letybo position themselves as premium choices, catering to consumers who prioritize top-tier products.
While foreign brands continue to dominate the high-end market for botulinum toxin products, Chinese brands are making strides in entering this space. Examples include Imeik’s ‘Orangedox’ in collaboration with Hunos and Hua Dong Medicine’s (华东医药) ‘Landox’ in partnership with Jetema. Despite being in the early stages of market promotion, these Chinese entrants currently hold relatively lower market shares.
Consumer demographics
The findings from Allergan Aesthetics’ consumer survey in China shed light on the diverse demographic landscape within the medical beauty industry. The sector is witnessing a notable shift towards a younger consumer base, indicative of the country’s evolving beauty standards and increasing acceptance of aesthetic enhancements.
Key consumer demographics insights include:
- Wide age spectrum: The allure of medical aesthetic procedures transcends age barriers, with individuals across various age groups actively incorporating these practices into their beauty regimens. This trend signifies a dynamic and inclusive approach to aesthetics across generations.
- Dominance of the ‘under-30 demographic’: Notably, young adults under the age of 30 emerge as the predominant consumers, constituting a significant portion of the surveyed medical aesthetic users in China. Generation Z (Gen Z), in particular, is at the forefront of this trend, consistently investing in both personal development and external appearance.
- Influence of abundant resources and information on Chinese Gen Z: The affluence of the Gen Z population in China translates into robust purchasing power within the medical beauty market. Leveraging the digital landscape, Chinese Gen Z individuals access a plethora of information channels, cultivating a consumption mindset that prioritizes self-improvement and comprehensive personal development.
- Increase in male consumers: Recent years have witnessed a significant uptick in male consumers engaging with the medical beauty industry. Notably, 2021 alone saw a remarkable 30 percent increase in male participation. What’s particularly interesting is the age distribution among these male consumers, with 45 percent of them falling into the age group above 30.
Market trends and consumer preferences
As consumer aesthetics and medical aesthetic technology continue to evolve, there is a noticeable surge in the popularity of non-surgical medical beauty procedures.
The thriving landscape of non-surgical treatments is driven by an active consumer base, and the three-year trend reflects a significant shift towards non-surgical interventions.
Prevalent non-surgical aesthetic trends include:
- Light medical aesthetic thrives: Consumers are increasingly drawn to light medical aesthetic treatments, with a focus on anti-aging and sculpting. This trend is attributed to the allure of low prices, minimal invasion, diversified treatment options, and the prospect of repeat consumption.
- Popular anti-aging and sculpting treatments: According to Allergan’s survey, Chinese consumers exhibit significant interest in non-surgical filling/sculpting, anti-wrinkle/anti-aging, and skin rejuvenation/brightening treatments. In particular, over 64 percent of consumers received filling/sculpting treatments, such as hyaluronic acid/collagen stimulant injections, and 68.72 percent received anti-wrinkle/anti-aging treatments, such as botulinum toxin injections in 2021.
- Male consumers and botulinum toxin: While female consumers exhibit diversified demands, male consumers show a greater preference for anti-wrinkle/anti-aging (Botulinum toxin) treatments, with 65 percent of them reporting such treatments in 2021.
- Rising interest in collagen: Collagen demonstrates strong market potential, especially among consumers over 26 years old.
Regulatory landscape
Over the past thirty years, several government departments, such as the State Council, the National Health Commission, the China Food and Drug Administration, and the Chinese Association of Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery, have implemented various detailed policies to foster the development of the medical beauty industry.
In 1994, the Ministry of Health published the Directory of Diagnostic and Treatment Subjects for Medical Institutions 《医疗机构诊疗科目名录》 officially designating the ‘Medical Aesthetic Department’ as a ‘Level One Diagnostic and Treatment Subject’ within medical institutions. Moreover, the ministry introduced the Basic Standards for Medical Institution 《医疗机构基本标准》outlining the initial standards for the medical aesthetic industry and related organizations. Following this, a series of regulations and guidelines have been gradually introduced. These include norms for institutional operations, standards for medical beauty services, and strengthening industry supervision. Recent examples are detailed in the table below.
| Regulations and Guidelines for China’s Medical Beauty Industry | ||
| Time | Plan/Policy | Key objectives |
| 2021 | Initiative on Regulating Financial Products and Financial Services Related to Medical Beauty
《关于规范医疗美容相关金融产品和金融服务的倡议》 Available here |
Promoting the development of financial products and services related to medical beauty and preventing practices such as “inducing consumers to over-borrow”. |
| 2022 | The 14th Five-Year Plan for the Construction of the Chinese Medical Beauty Standard System
《中国医疗美容标准体系建设“十四五”规划》 Available here |
Objectives include, among others:
|
| 2022 | 2022 Medical Aesthetics Institution Standardized Operations Guidelines
《2022 年医疗美容机构规范运营指南》 Available here |
Amidst the sector’s exponential growth driven by unprecedented consumer demand, objectives involve:
|
It is important to note that, since 2021, the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) released guidelines categorizing medical beauty advertising as equivalent to medical advertising. This move places medical beauty advertisers under the same regulatory scrutiny as their medical counterparts, requiring them to obtain special licensing before disseminating advertisements.
The newly introduced Medical Beauty Advertising Law Enforcement Guide emphasizes the need for standardization and consumer protection. To comply with the regulations, medical beauty advertisers must acquire a license for advertising, ensuring that their advertisements adhere to specific guidelines. These guidelines prohibit the promotion of unapproved products, the creation of ‘appearance anxiety,’ and the disguised presentation of advertisements as interviews or reports.
Industry challenges and opportunities
China’s medical beauty industry presents several key challenges, including:
- Shortage of professional practitioners: One significant challenge facing the medical beauty industry in China is the shortage of qualified and skilled practitioners. The demand for aesthetic procedures has surged, but there is a notable gap in the number of professionals available to meet this demand. This shortage not only affects the accessibility of services but also raises concerns about the quality of treatments provided.
- Lack of comprehensive and institutionalized professional training system: The industry grapples with the absence of a well-established and comprehensive professional training system. While the demand for medical beauty services is escalating, the lack of standardized training programs for practitioners poses a hindrance. A structured training system is crucial to ensure that practitioners acquire the necessary skills, knowledge, and ethical standards, contributing to the overall enhancement of service quality.
On the other hand, the sector also seems to present a vast array of opportunities for businesses and investors, including:
- Market growth projections: On a more optimistic note, market forecasts paint a picture of substantial growth, with expectations that the industry will exceed RMB 500 billion (US$70.5 billion) by 2028.
- Changing consumer dynamics: Consumer attitudes toward medical beauty products and services are undergoing a significant shift. Factors such as rising disposable income, consumer upgrading trends, and the influence of digital marketing have collectively contributed to an increased acceptance of these services. This evolving consumer landscape presents an opportune moment for industry players to tailor their offerings to meet changing preferences.
- Innovation and expansion: The industry’s dynamism is evident in the continuous innovation of commercialized medical beauty products and the expansion of service offerings. This not only keeps the industry fresh and appealing but also opens avenues for businesses to differentiate themselves through unique and cutting-edge solutions.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates also has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Dubai (UAE). We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China Tax Risks in Indirect Equity Transfer: A Case Study
- Next Article Q&A: How to Apply for the GBA IIT Subsidy in Dongguan City







