Investing in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province: China City Spotlight
Hangzhou, capital city of Zhejiang Province and home to e-commerce giant Alibaba, offers a unique blend of tradition and technology. It is also one of the most prosperous cities in the Yangtze River Delta and a recognized new first tier city in China. We explore the city’s thriving tech ecosystem as well as investment incentives and the various development zones, which make it a top destination for foreign investors.
Hangzhou, the capital city of Zhejiang province, has become globally well-known since hosting the G20 Summit in 2016. Leveraging its strategic location at Hangzhou Bay, nestled between the bustling metropolises of Shanghai and Ningbo, the city has established itself as a beacon of economic prowess and technological innovation in the dynamic landscape of the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region.
With an inviting business environment characterized by lower office setup costs than its neighboring financial hub Shanghai, an array of competitive government tax incentives, and a robust network of local IT companies, Hangzhou stands out as an alluring investment destination for both domestic and international investors, accounting for nearly 25 percent of the whole province’s economic output each year.
Notably, the city serves as the proud headquarters for Alibaba, the pioneering e-commerce and tech giant that has revolutionized digital commerce on a global scale.
Hangzhou’s economic profile
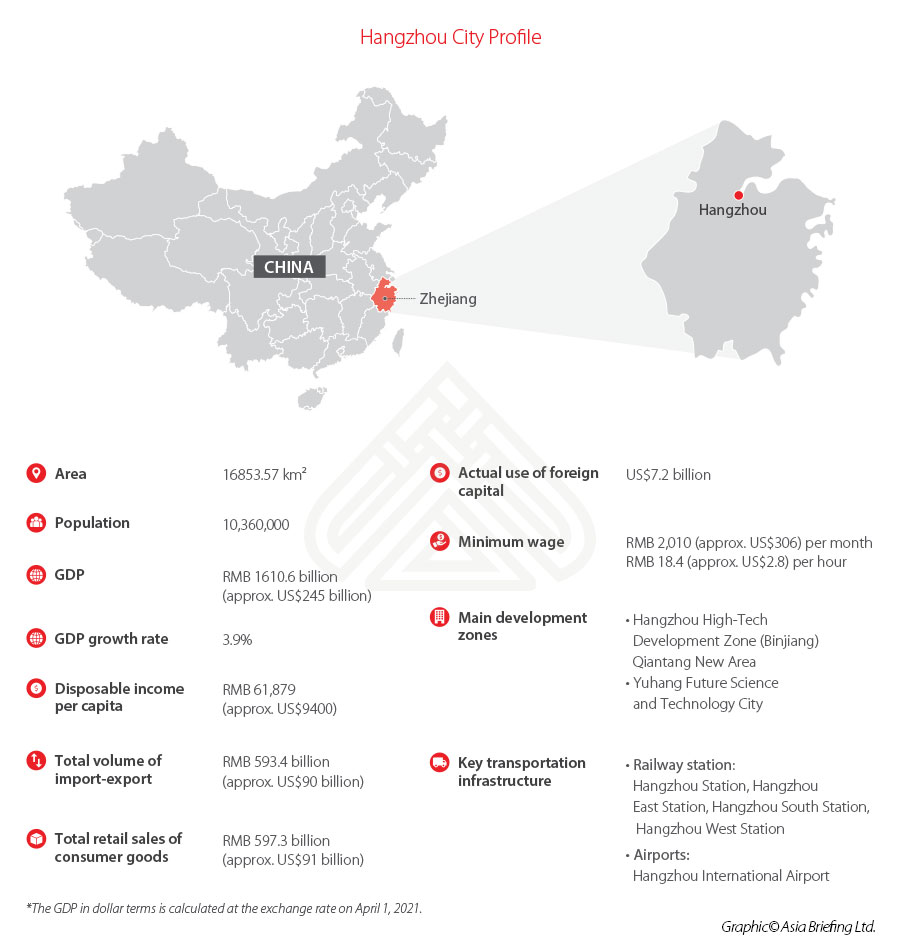
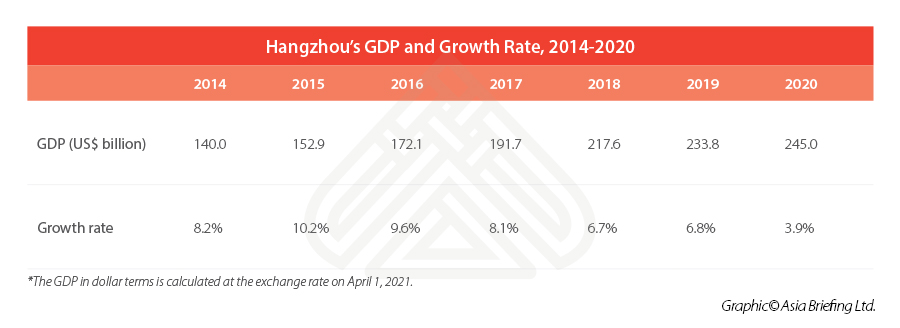
According to the data related by the Hangzhou Municipal Bureau of Statistics, in 2022, Hangzhou’s GDP reached RMB 1,875 billion (approx.US$246.12 billion), making it the fourth provincial capital city with the largest GDP in the Chinese Mainland. For perspective, that’s about the size of the Czech Republic’s or Portugal’s economy. Hangzhou is also one of the top three cities in the Yangtze River Delta region in terms of GDP, next only to Shanghai and Suzhou.
Located in the most affluent region of east China, Hangzhou’s permanent resident per capital GDP as of 2022 is over US$22,600, which is comparable to the level of high-income countries, according to the World Bank. In 2022, the total retail sales of consumer goods in Hangzhou reached RMB 724 billion (US$106.4 billion), registering a robust 5.8 percent increase compared to 2021, thereby positioning the city as a leader in terms of growth rate among various cities in China.
In 2022, the core digital economy industries saw a 2.8 percent rise, with an added value of RMB 507.6 billion (US$69.34). Particularly, the manufacturing sector within the digital economy witnessed a significant 4.4 percent growth, amounting to an added value increase of RMB 118 billion (US$16.12 billion).
Moreover, the private sector played a pivotal role, accounting for 50.7 percent of the total fixed asset investment, an increase of 1.1 percentage points from 2021.
Foreign trade and investment
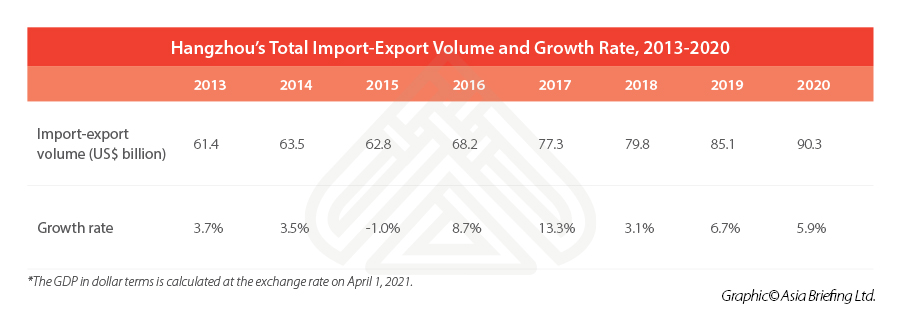
In 2022, Hangzhou witnessed a total import and export volume of RMB 756.5 billion (US$103.35 billion), marking a 2.7 percent growth compared to the previous year. Specifically, exports accounted for RMB 514.1 billion (US$70.23 billion), representing a substantial 10.6 percent increase, while imports totaled RMB 242.4 billion (US$33.11 billion), reflecting a decrease of 10.8 percent.
The city’s exports to countries along the Belt and Road Initiative amounted to RMB 168.8 billion (US$21.86 billion), showing a significant growth of 12.9 percent. Notably, exports to the European Union, the United States, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Latin America, and Africa recorded growth rates of 5.4 percent, 6.2 percent, 18 percent, 13.5 percent, and 16.8 percent, respectively.
Furthermore, the export of high-tech products surged to RMB 104.1 (US$14.22 billion), marking a substantial 14.7 percent increase and accounting for 20.2 percent of the city’s total export value, a 0.7 percentage point increase from the previous year.
As an e-commerce hub, Hangzhou’s imports and exports through cross-border e-commerce alone totaled RMB 120.3 billion (US$15.5 billion), up 8 percent from the previous year.
In 2022, Hangzhou attracted 840 new foreign investment projects, including 97 valued at over US$30 million and 29 worth over US$100 million. The city utilized US$7.81 billion in foreign investment, with US$4.59 billion focused on high-tech industries, a 14.2 percent increase from 2021.
Throughout the year, Hangzhou welcomed investments from 9 Fortune 500 companies, contributing to a total of 234 projects by 134 such companies in the city.
The city established 3,002 overseas investment enterprises and institutions, marking an 11.1 percent increase from the previous year. International economic cooperation reached a turnover of US$1.44 billion. The total overseas investment for the year amounted to US$4.55 billion, with $2.68 billion from domestic investments. Additionally, the offshore service outsourcing contract execution value reached US$8.82 billion, indicating a 6.3 percent growth.
Industry development
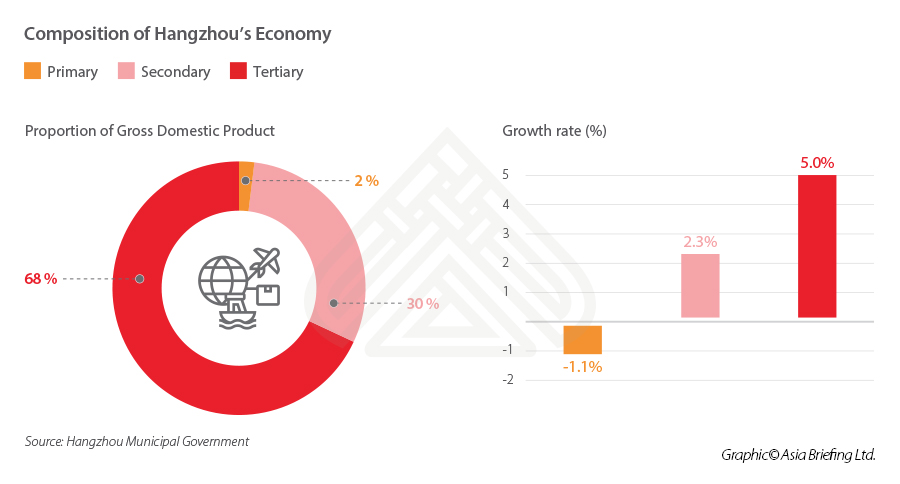
Hangzhou’s digital economy is the leading contributor to its overall economy. In 2020, core digital industries added value of RMB 429 billion (US$65.5 billion), up 13.3 percent and contributing to 26.6 percent of its total GDP, an increase from 24.7 percent in 2019.
Growth in related sectors like manufacturing of electronic information products, software and information services, digital contents, and robotics were 14.7 percent, 12.9 percent, 12.7 percent, and 12.3 percent, respectively.
Financial services and the digital economy
Over the years, Hangzhou’s financial industry has transitioned from a singular to a multifaceted service provider. It has gained recognition for its prowess in the financial technology domain and has solidified its position as one of the top five cities in the country in terms of comprehensive financial competitiveness.
With a focus on constructing a unified and coordinated development pattern, Hangzhou has strategically established various financial service platforms, including the Qianjiang Financial Port and multiple distinctive financial agglomeration areas throughout the city.
In particular, the added value of the core digital economy industry reached RMB 507.6 billion (US$70.60 billion), an increase of 2.8 percent over the previous year.
Electronic information manufacturing
Hangzhou is among the seven main centers in China for integrated circuit design. The city boasts national industrial parks dedicated to telecommunication and optical fiber optic cable industries. It is recognized as a top player in network communication technology and products, along with fiber optic cable manufacturing. Additionally, Hangzhou’s routers and switches hold a significant market share globally, ranking among the top three.
At the forefront of this thriving industry are several prominent companies that have significantly contributed to Hangzhou’s reputation as a technological powerhouse. These include:
- New H3C Group (New H3C): New H3C is engaged in researching, developing, producing, and selling innovative IT solutions, including networks, servers, storage products, and IT management systems.
- Eastcom: Its product range encompasses specialized network communication, information security solutions, financial electronic equipment, communication and IT services, and MES manufacturing.
- Silan Microelectronic: Silan Microelectronic is renowned for its expertise in IC chip design and semiconductor microelectronics. It holds a prominent position as one of China’s leading integrated circuit chip designers and manufacturers, with a substantial production capacity for chips under six inches. This has bolstered Hangzhou’s reputation as a key player in the global semiconductor industry.
- Hangzhou Futong Showa Optical Communication Co. (FSO): FSO specializes in optical fiber prefabrication sticks and optical fiber production.
E-commerce and high-tech
The emergence of Hangzhou’s tech industry owes much to being the birthplace of Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba, which owns e-commerce websites Taobao and Tmall, digital financial service giant Ant Group which owns Alipay, and clouding computing company Aliyun.
Leading Chinese electronic IT companies based in Hangzhou, like Aliyun, Hikvision, Dahua Technology, and Uniview, hold a sizeable market share in global markets. To be noted, Hikvision and Dahua Technology are among Chinese high-tech companies that are sanctioned and blacklisted by the US amid the deepening US-China tech rivalry.
As a city famous for its high-tech sector, the Hangzhou government actively promotes its smart city program. Alibaba and 13 other companies are now working with the local government on public private partnerships (PPP) to create smart service delivery systems for the city.
For instance, Hangzhou on Palm, the world’s largest smart-app-based public bicycle system, has 3,8000 bicycles stationed at 2,500-plus docking points. The Hangzhou City Brain, driven by the Alibaba Group, aims to build “one network”, “one cloud”, “one data bank”, and “one nerve center”, which processes over 7.6 million API (Application Programming Interface) calls and 120 million collaborative data each day, to offer Hangzhou solutions for digitalize governance of large cities.
Where to locate your investment: Hangzhou’s development zones
As of 2023, Hangzhou boasts a total of seventeen development zones, including nine state-level and four provincial-level zones. To encourage enterprises to set up in Hangzhou and its development zones, the local government provides tax breaks for high-tech firms, with additional incentives for internet start-ups, including housing subsidies for entrepreneurs and events to promote private and foreign investment to support start-ups.
Hangzhou high-tech Development Zone (Binjiang) and Hangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone are among the top ranked in the comprehensive ranking of national high-tech zones and annual assessment of national economic development zones.
Hangzhou High-tech Industry Development Zone (Binjiang)
The Hangzhou High-tech Industry Development Zone (Binjiang) houses over two-thirds of the city’s tech companies.
With a growing emphasis on the integration of digital technology into traditional manufacturing, Binjiang has established itself as a thriving industrial ecosystem, specializing in intelligent Internet of Things, smart manufacturing, and digital health services. Emphasizing its status as a burgeoning digital economy development and smart manufacturing stronghold, the district has become a beacon for global talent seeking to contribute to its dynamic landscape.
Home to pioneering entities like Zhejiang Geely Holding Group and Leapmotor, Binjiang has fostered a conducive environment for innovation and growth, attracting top-tier research and development talent. The district’s proactive initiatives, such as talent fostering programs and venture capital support, have contributed to the meteoric rise of numerous high-tech enterprises, propelling the area’s transformation into a burgeoning tech incubator akin to the renowned Silicon Valley.
Notable investors in this zone include Alibaba, Microsoft, IBM, Nokia, Panasonic, and Mitsubishi.
Beyond its industrial prowess, Binjiang prides itself on providing a well-rounded living experience for its residents. Its picturesque riverside setting offers an array of recreational amenities, including expansive parks and vibrant running tracks that underscore its reputation as a “paradise” for sports enthusiasts. Notably, the district’s Hangzhou Olympic Sports Center Stadium, Tennis Center Finals Hall, and Binjiang District Stadium, all set to host events during the upcoming 19th Asian Games, stand as testaments to its commitment to fostering a healthy and active lifestyle among its residents.
Hangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone
Established in 1993 and approved by the State Council, the Hangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone stands as a beacon of technological advancement and industrial progress within the region.
The development zone is home to five key industries that form the cornerstone of its economic prowess. These include electronic engineering, biological medicine, textile and chemical fiber, light industry and food, and high-tech chemical industries. These diverse sectors collectively contribute to the zone’s vibrant economic landscape, fostering an environment conducive to both technological innovation and industrial production.
With its strategic positioning and diverse industrial portfolio, the development zone continues to play a pivotal role in propelling Hangzhou’s economic and technological landscape forward, nurturing an environment conducive to innovation, industrial excellence, and global competitiveness.
Qiantang New Area
In April 2019, Hangzhou established the Qiantang New Area, which incorporates Hangzhou Dajiangdong Industry Cluster Zone and Hangzhou Economic and Technological Development Area.
With the goal of becoming a world-class intelligent manufacturing industrial center, Qiantang New Area has attracted big brands like Pfizer, Bayer, Geely, and Gree from various advance manufacturing industries, including semi-conductor, life and health, new materials, aerospace and aviation, and intelligent automobile and intelligent equipment industries.
On February 21, 2023, Qiantang approved the inception of 22 significant projects, with a cumulative investment totaling RMB 30.8 billion (US$4.2 billion). These projects encompass 11 industrial development initiatives, valued at RMB 12.9 billion (US$1.76 billion), 2 social undertakings valued at RMB 1.2 billion (US$163.95 million), 2 infrastructure projects valued at RMB 8.1 billion (US$1.1 billion), and 7 urban functional projects amounting to RMB 8.6 billion (US$1.17 billion).
One of the notable industrial projects, the High Innovation World Industrial Park, boasts a total investment of RMB 2.39 billion (US$326.54 million). The park is envisioned to become a comprehensive industrial hub, hosting benchmark corporate headquarters, fostering intelligent manufacturing research and development, and nurturing young entrepreneurial talent. The project is slated for completion by June 2026.
Xiaoshan Economic and Technological Development Zone
The Xiaoshan Economic and Technological Development Zone (XETDZ), established in Hangzhou, Zhejiang province in May 1990, was elevated to the status of a State-level economic and technological development zone following approval by the State Council in 1993.
Encompassing a vast area of 110 square kilometers, XETDZ is divided into four key areas: Shibeicheng, Qiaonancheng, Kejicheng, and Yinong.
Strategically positioned at the heart of the Yangtze River Delta region on the southeast coast of China, the zone benefits from its advantageous geographic location and excellent transportation connectivity. Notably, it enjoys seamless access to fifteen major cities within a three-hour drive and is situated just a 15-minute drive away from the Hangzhou Xiaoshan International Airport, a key aviation hub in China.
With more than two decades of development, the XETDZ has evolved into an export-oriented modern industrial park, excelling in diverse sectors such as machinery manufacturing, electronic facility manufacturing, textiles, automobile and parts manufacturing, medicine, food, furniture, new materials, and new energy.
Since its establishment in 1993, the economic output of the development zone has witnessed an impressive growth trajectory, surging from RMB 205 million (US$29 million) to a remarkable RMB 73.361 billion (US$10 billion) in 2022.
XETDZ has successfully attracted 651 foreign-funded projects, establishing itself as the seventh largest contributor to foreign investment utilization in China. Moreover, the zone remains dedicated to fostering the growth of its internet-based platform economy, simultaneously enhancing collaboration with other regional sectors.
Xiaoshan has also recently become home of China’s (Hangzhou) 5G Innovation Valley. Born in 2019 from a collaborative effort between Xiaoshan district, the Hangzhou 5G Research Institute, Winreal Investment Co, and the Zhejiang Torch Center, the valley accommodates over 1,500 skilled workers and hosts 38 companies focusing on 5G technology, six of which have been acknowledged as national high-tech entities.
Notably, the valley has facilitated the creation of 337 intellectual property rights, while these companies have collectively attracted over RMB 350 million (US$52.26 million) in financing.
Yuhang Future Science and Technology City, and the Digital Health Town
Another key development zone is the Yuhang Future Science and Technology City. On April 28, 2020, Yuhang Future Science and Technology City embraced its first livestreaming e-commerce industry base, aimed to boost Hangzhou’s e-commerce economy.
To encourage enterprises to set up in Hangzhou and its development zones, the local government provides tax breaks for high-tech firms, with additional incentives for internet start-ups, including housing subsidies for entrepreneurs and events to promote private and foreign investment to support start-ups.
In August 2020, the Digital Health Town emerged as a focal point within the Yuhang Future Science and Technology City, serving as a significant nexus for the integration of the digital economy and life health sectors. Encompassing an expansive area of 3.2 square kilometers, the town has been strategically designed to facilitate the rapid development of pivotal projects.
With core elements like an integrated research center, enterprise R&D headquarters, and achievement transformation area, the town is fostering collaborations among renowned educational institutions and research organizations.
Currently hosting 24 projects, including those focused on smart healthcare and advanced diagnostic and treatment solutions, the town is positioned to enhance the district’s technological and industrial landscape.
City-wide policies and incentives
As a city renowned for its forward-thinking mindset and technological advancements, Hangzhou has been actively implementing a series of progressive policies and incentives to bolster its economic growth and foster a conducive environment for innovation and development.
With a keen focus on enhancing investment opportunities, fostering technological breakthroughs, and cultivating key industries, Hangzhou has emerged as a frontrunner in promoting an ecosystem that encourages both local and foreign enterprises to thrive.
Recently implemented policies have been highlighted in the table below.
|
Hangzhou City-Wide Incentive Policies |
|
| Policy | Measures |
| Several Policies on Promoting High-Quality Economic Development
《关于推动经济高质量发展的若干政策》 Available here |
Measures cover several key areas.
Expanding effective investment policy, includes:
Technological innovation policy, includes:
High-quality development policy for the modern service industry, includes:
Encouraging major software product innovation in fields such as AI, big data, and blockchain.
Enhancing cross-border trade Facilitation:
Optimizing Management of Foreign Investment and International Talent Services:
|
| Hangzhou National Business Environment Innovation Pilot Implementation Plan
《杭州市国家营商环境创新试点实施方案》 Available here |
Measures cover several areas.
Eliminating unreasonable restrictions:
Improving Transparent and Efficient Market Access and Exit Mechanisms:
Enhancing cross-border trade Facilitation:
Optimizing Management of Foreign Investment and International Talent Services:
|
| Hangzhou City’s Plan for Promoting High-Quality Economic Development – ‘Phoenix Action’ (2021-2025)
杭州市深入推进经济高质量发展“凤凰行动”计划(2021—2025年) Available here |
Objectives include
|
2023 Hangzhou Asian Games
As the guest city of the 19th Asian Games (hereinafter referred to as “Games”) in 2023, Hangzhou has experienced a significant boost across various economic sectors and industries. The event has driven considerable growth in tourism, sports-related consumption, and the overall development of the sports industry in Hangzhou. This boost in tourism and sports-related activities has also has a cascading effect on the local economy, leading to increased revenue for businesses in the hospitality, retail, and service sectors.
In anticipation of the Games, from January to June 2023, the city had already received a total of about 53 million tourists, with the sector reaching a total revenue of RMB 91.5 billion yuan (US$12.76 billion), a yearly increase of 64.5 percent and 65.3 percent respectively.
The increased emphasis on sports and fitness, as witnessed during the Asian Games, is expected to contribute to a heightened demand for sports equipment, apparel, and related merchandise. This surge in sports-related consumption can provide opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs to cater to the growing market of sports enthusiasts and athletes.
Moreover, the implementation of robotics and smart technologies during the Asian Games can also serve as a catalyst for the automation industry, presenting opportunities for the development and implementation of advanced robotics solutions across various sectors.
Overall, the Games are expected to leave a positive and long-lasting impact on Hangzhou’s economy, contributing to its growth and development across multiple sectors, and offering a wide array of opportunities for businesses and investors.
This article was originally published on April 6, 2021, and last updated on October 30, 2023.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article Unveiling Business Synergies: Exploring the Complementary Relationship Between the Greater Bay Area and Vietnam
- Next Article Foreign Investment into China Falls as Capital Sources Change